MethSCAn
a command line tool for Single-Cell Analysis of Methylation data.
Installation
This software requires a working installation of Python 3 (≥3.8) and requires the use of a shell terminal. It was extensively tested on Linux (Ubuntu 18, 20 and 22) and MacOS, and briefly tested on Windows 10.
You can install MethSCAn from the Python package index as follows:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip # you need a recent pip version
python3 -m pip install methscan
Installation of MethSCAn should take no longer than a few seconds. All required dependencies are automatically installed, this may take a few minutes.
Afterwards, restart your terminal. The installation is now finished and the command line interface should now be available when typing the command methscan in your terminal.
If this is not the case, check the “troubleshooting” section below.
Updating to the latest version
Just use --upgrade when installing the package, otherwise it’s the same process as installing:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade methscan
Afterwards, make sure that the latest version is correctly installed:
methscan --version
Tutorial of a typical methscan run
A tutorial / demo can be found here. This gives instructions on how to use MethSCAn on a small example data set which we provide.
Also make sure to read the help by typing methscan --help or by checking this page.
What can this package do?
MethSCAn takes as input a number of single-cell methylation files and allows you to quickly and easily obtain a cell × region matrix for downstream analysis (e.g. PCA, UMAP or clustering). It also facilitates quality control, allows you to discover variably methylated regions (VMRs), accurately quantifies methylation in genomic intervals, and stores your sc-methylomes in an efficient manner. Lastly, you can also select two cell populations and identify differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between them.
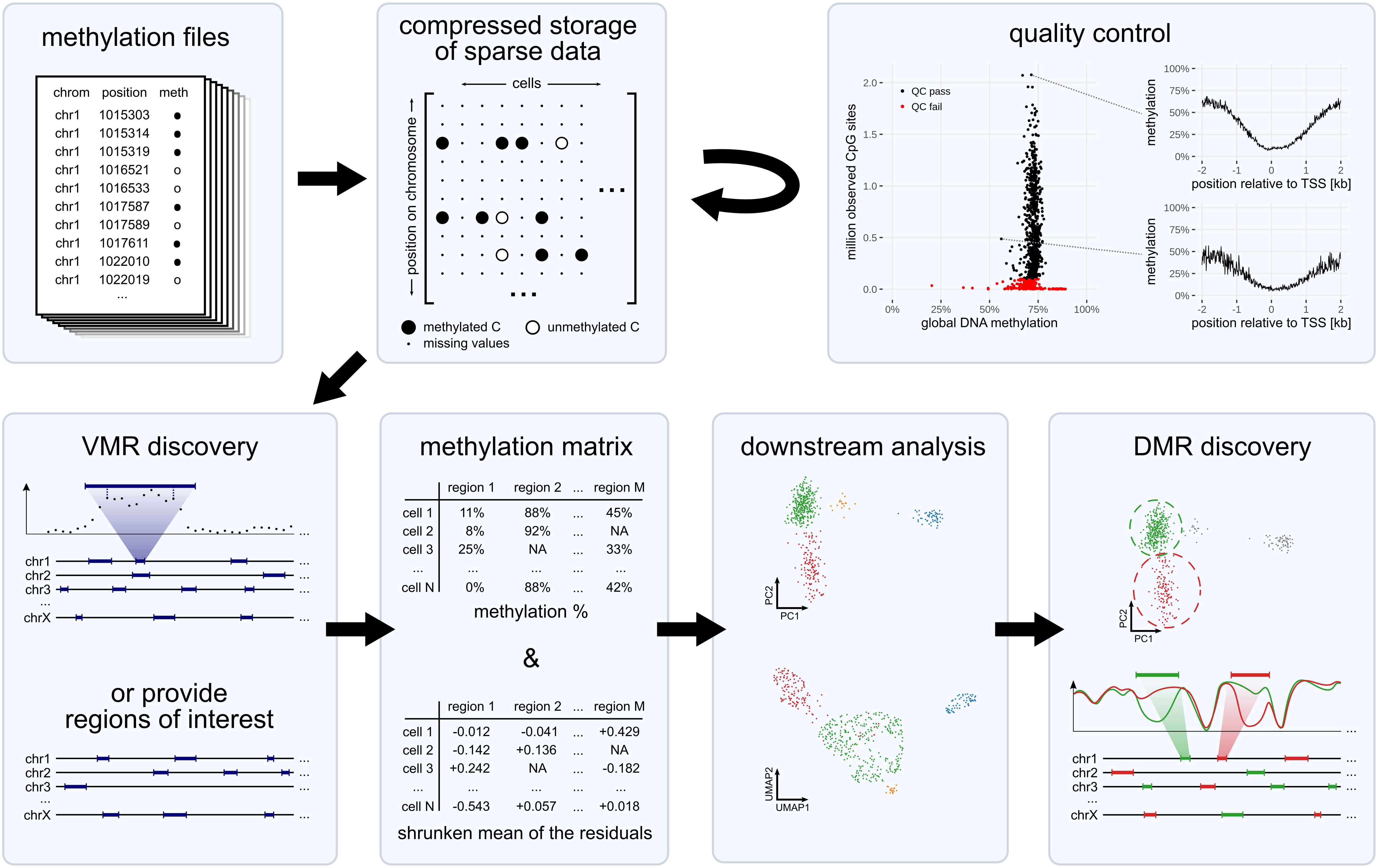
You can find a list of the available methscan commands here.
Publication / Citation
For a detailed explanation of the methods implemented in MethSCAn, please check out our open access article in Nature Methods:
Analyzing single-cell bisulfite sequencing data with MethSCAn
Lukas PM Kremer, Martina Braun, Svetlana Ovchinnikova, Leonie Kuechenhoff, Santiago Cerrizuela, Ana Martin-Villalba, Simon Anders.
Nature Methods, 2024
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-024-02347-x
Please cite this article if you used MethSCAn in your research.
Note that this package was formerly known as ‘scbs’ and later renamed to MethSCAn.
Hardware requirements
For intermediate data sets consisting of 1000 to 5000 cells, we recommend to use a computer with at least 16 gigabytes of RAM.
Very large data sets (~100k cells) require at least 128 GB.
Multiple CPU cores are not strictly required but will greatly speed up some commands such as methscan scan or methscan diff when using the --threads argument.
FAQ
What’s the difference between a VMR and DMR?
Variably methylated regions (VMRs) are genomic intervals that exhibit variable levels of methylation across the cells in a given sample. In simple words, this means that some cells exhibit high methylation in this region, while other cells exhibit low methylation there. The VMR detection algorithm is not concerned with the source of this variation: it could be due to differences in cell type, data quality, or any other factor that might affect DNA methylation. In contrast, differentially methylated regions (DMRs) are the result of a targeted comparison of two groups of cells that were manually selected by the user (e.g. wild type cells vs. knockout cells, cancer vs. healthy, neurons vs. astrocytes). If you are familiar with scRNA-seq, it makes sense to think of DMRs as similar to differentially expressed genes, while VMRs are similar to highly-variable genes.
Troubleshooting
Installation issue “This environment is externally managed”
The latest Ubuntu version requires the use of a virtual environment to install Python packages.
In almost all cases, this can be achieved by using pipx instead of pip. To do this, install pipx if you don’t have it already.
Then you can install MethSCAn with pipx install methscan. Then restart your terminal.
For more information or alternative solutions, check this answer on stackoverflow.
Other installation issues
Carefully check the output log of PIP. Look for a message like WARNING: The script methscan is installed in '/home/ubuntu/.local/bin' which is not on PATH., which would indicate that you need to add /home/ubuntu/.local/bin to your path. Alternatively, you can copy /home/ubuntu/.local/bin/methscan to e.g. /usr/local/bin.
If you encounter other problems during installation, make sure you have Python3.8 or higher, and make sure you have the latest PIP version. If the problem persists, consider installing methscan in a clean Python environment (for example using venv).
Too many open files
If you encounter a “too many open files” error during methscan prepare (OSError: [Errno 24] Too many open files), you need to increase the maximum number of files that can be opened. On Unix systems, try ulimit -n 99999.
Source Code
The source code is hosted at the GitHub repository anders-biostat/MethSCAn.
Authors
- Lukas PM Kremer
- Martina Braun
- Svetlana Ovchinnikova
- Leonie Küchenhoff
- Santiago Cerrizuela
- Ana Martin-Villalba
- Simon Anders
Developed in the Anders lab and the Martin-Villalba lab.


